Medical Coding: A Complete Guide to Career, Process, and Scope
Discover everything about medical coding — its meaning, process, job opportunities, certifications, and future in healthcare.
Introduction
In today’s digital healthcare environment, accurate record-keeping and claim management have become essential. Medical coding plays a key role in transforming healthcare diagnoses, procedures, and services into universally recognized alphanumeric codes. This helps hospitals, insurance companies, and government health departments maintain a uniform record system for billing, reporting, and data analysis.
Every time a patient visits a doctor, undergoes a test, or receives a treatment, the details are documented in medical records. To ensure that these details can be processed efficiently by insurance systems and health databases, medical coders assign specific standardized codes to each service and diagnosis.
What is Medical Coding?
Medical coding is the process of converting healthcare diagnoses, procedures, medical services, and equipment into standard medical codes. These codes are derived from universal classification systems such as:
- ICD (International Classification of Diseases): Identifies diagnosis and disease conditions.
- CPT (Current Procedural Terminology): Describes the procedures and services provided.
- HCPCS (Healthcare Common Procedure Coding System): Covers products, supplies, and services not included in CPT codes.
By converting medical data into these standardized codes, the healthcare industry ensures consistency in billing, data tracking, and patient care reporting across the world.
History and Evolution of Medical Coding
The concept of medical coding dates back to the early 20th century when healthcare professionals needed a uniform way to classify diseases and causes of death. The World Health Organization (WHO) introduced the first version of the International Classification of Diseases (ICD) in the 1940s to collect global health data.
Over the years, medical coding evolved to support modern healthcare demands. The development of CPT codes in the 1960s by the American Medical Association made it possible to classify medical procedures for billing purposes. With the rise of digital healthcare records and insurance systems, the role of coders became crucial in managing both clinical and financial aspects of patient care.
Importance of Medical Coding in Healthcare
Medical coding is not just about billing—it’s the foundation of the entire healthcare revenue cycle. Every hospital, clinic, and diagnostic center relies on coders to ensure accurate claim submissions and maintain compliance with health data standards.
- Ensures Accurate Billing: Correct codes prevent claim rejections and financial losses.
- Supports Public Health Data: Helps in tracking disease trends, epidemics, and healthcare utilization.
- Improves Patient Care: Consistent coding assists in quality control and performance improvement.
- Maintains Legal Compliance: Prevents fraudulent billing and ensures ethical documentation.
In short, medical coding acts as a bridge between healthcare providers, insurance companies, and government health organizations, ensuring smooth communication and proper reimbursement.
How Medical Coding Works
The process of medical coding begins the moment a patient interacts with the healthcare system — whether through a doctor’s visit, a diagnostic test, or a surgical procedure. Each encounter generates detailed documentation known as a medical record. This record includes the patient’s symptoms, medical history, test results, and treatments provided.
A medical coder reviews this documentation carefully and identifies the elements that need to be translated into standardized codes. The coder ensures that each diagnosis, treatment, and procedure performed by healthcare professionals is accurately represented using globally accepted classification systems.
Once coded, these codes are entered into hospital billing or insurance software, where they are used to generate claims and analyze health data. Proper coding ensures that healthcare providers are paid correctly and patients receive the benefits covered by their insurance plans.
Types of Medical Codes
Medical coding uses different code sets for various purposes. Each type of code has its own structure, usage, and purpose within healthcare operations. The three most common types of codes are ICD, CPT, and HCPCS.
1. ICD Codes (International Classification of Diseases)
ICD codes are used to represent diagnoses and medical conditions. Developed by the World Health Organization (WHO), these codes are globally recognized and help in recording and analyzing health conditions statistically. The current version, ICD-10, contains more than 70,000 codes that describe specific diseases and symptoms.
Example: E11.9 — Type 2 diabetes mellitus without complications.
2. CPT Codes (Current Procedural Terminology)
CPT codes are maintained by the American Medical Association (AMA) and are used to describe medical, surgical, and diagnostic services. They are essential for billing purposes and ensure uniform reporting of healthcare services.
Example: 93000 — Electrocardiogram (ECG) routine with interpretation and report.
3. HCPCS Codes (Healthcare Common Procedure Coding System)
HCPCS codes are primarily used to represent non-physician services, medical supplies, and equipment such as wheelchairs, bandages, or injections. These are often used for Medicare and Medicaid billing in the United States.
Example: A0428 — Ambulance service, basic life support, non-emergency transport.
4. DRG Codes (Diagnosis Related Groups)
DRG codes are used by hospitals to classify patients into groups based on diagnosis, treatment, and resource usage. This helps determine hospital reimbursement rates under insurance or government health schemes.
Example: DRG 291 — Heart failure and shock with major complications.
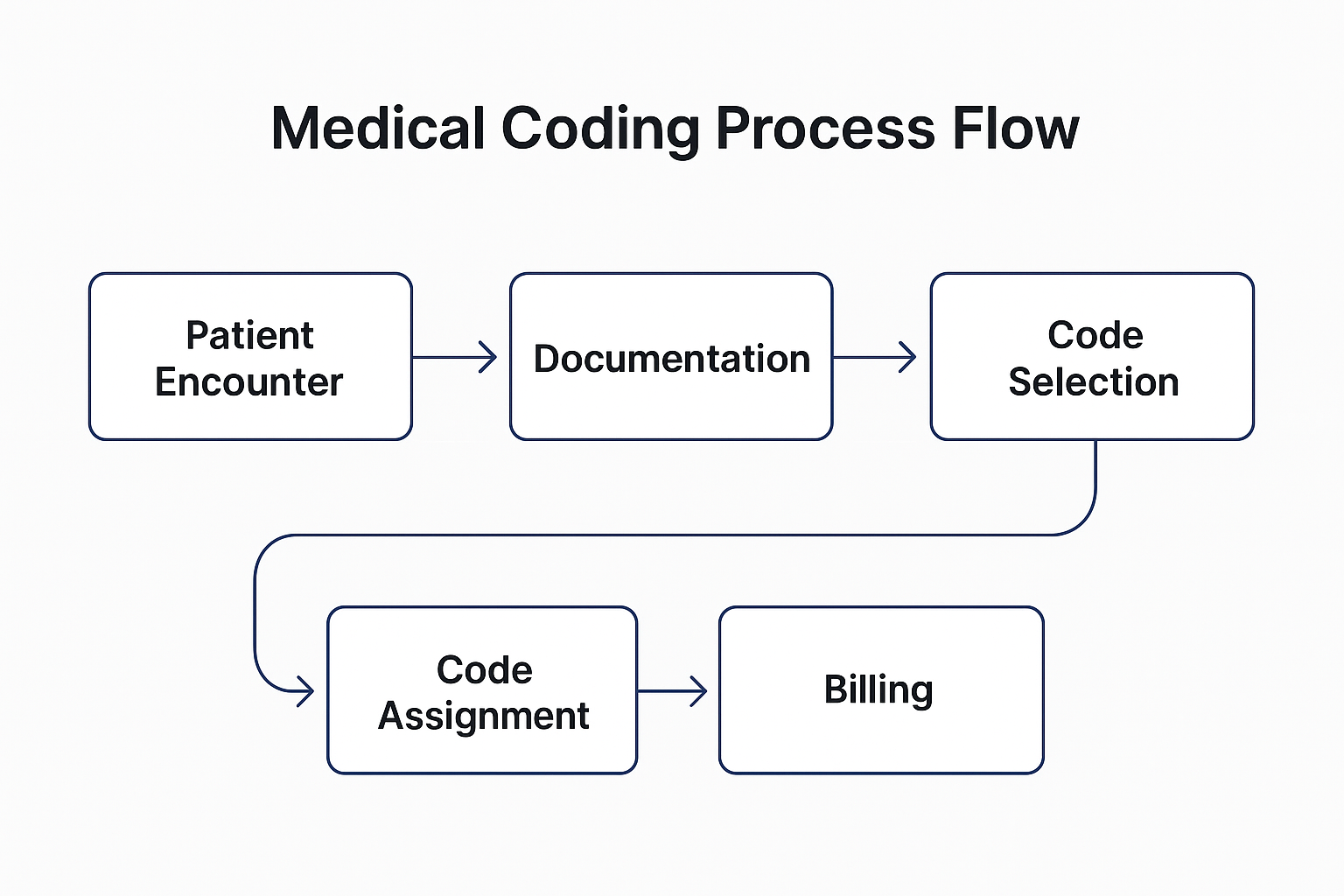
Step-by-Step Process of Medical Coding
Understanding how coding fits into the healthcare workflow is essential. The medical coding process usually follows a systematic approach involving multiple stages.
- 1. Patient Visit and Documentation: Every patient encounter generates documentation, including medical notes, test reports, and physician observations.
- 2. Record Review by Coder: The coder reviews the patient’s chart or electronic medical record (EMR) to identify relevant details such as diagnosis, procedures, and treatments.
- 3. Code Assignment: The coder assigns the appropriate ICD, CPT, or HCPCS codes based on the information available.
- 4. Data Verification: The assigned codes are verified to ensure accuracy and compliance with guidelines from organizations such as WHO, AMA, or CMS.
- 5. Claim Submission: The coded information is sent to the billing department or directly to the insurance provider for reimbursement processing.
- 6. Feedback and Correction: If the insurance company identifies an error or discrepancy, the coder reviews and corrects the claim before resubmission.
Medical Coding in Hospitals and Clinics
In large hospitals, coding is often handled by a team of professionals who specialize in specific departments such as surgery, radiology, or oncology. In smaller clinics, a single coder might manage all aspects of coding and billing. Accuracy is critical at all levels because even a minor error can delay payment or cause claim denials.
Modern healthcare systems use specialized software and AI-assisted coding tools to minimize human errors and increase efficiency. However, human coders remain essential because they interpret complex medical terminology and ensure context-based accuracy.
Medical Coding vs. Medical Billing
While medical coding and medical billing are often mentioned together, they represent two distinct but interrelated functions within the healthcare revenue cycle. Both roles ensure that healthcare providers are properly reimbursed for their services, yet the focus and responsibilities differ significantly.
| Aspect | Medical Coding | Medical Billing |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Translates healthcare documentation into standard codes. | Submits coded data to insurance companies for claim processing. |
| Work Focus | Accuracy of codes for diagnoses and procedures. | Accuracy of claim forms, payments, and follow-up. |
| Tools Used | ICD, CPT, and HCPCS code books or software. | Insurance claim software and electronic health records (EHR). |
| End Goal | Ensure proper representation of medical information. | Ensure proper reimbursement for healthcare services. |
| Work Environment | Hospitals, clinics, coding companies, or remote setups. | Hospital billing departments, insurance firms, or third-party billing companies. |
In simple terms, medical coders transform medical information into standardized codes, while medical billers use those codes to prepare and submit insurance claims. Both roles require collaboration and precision, as even minor mistakes can delay payments or create compliance issues.
Skills Required for a Successful Career in Medical Coding
Medical coding demands a unique mix of technical, analytical, and communication skills. Coders must be comfortable working with detailed medical records and complex healthcare terminology while ensuring 100% accuracy.
- Knowledge of Anatomy and Physiology: Understanding how the human body works is crucial for accurate code assignment.
- Strong Analytical Skills: Coders must interpret detailed medical notes, identify key elements, and match them with the correct code sets.
- Attention to Detail: Even a small coding error can lead to claim rejection or compliance issues.
- Computer Proficiency: Familiarity with healthcare software, EHR systems, and coding platforms is essential.
- Ethical Awareness: Coders must maintain confidentiality and adhere to healthcare privacy laws such as HIPAA.
- Communication Skills: Effective interaction with doctors, nurses, and billing professionals ensures clarity and accuracy.
Courses and Training in Medical Coding
Medical coding can be learned through dedicated diploma programs, online certifications, or professional training courses. These programs focus on teaching coding systems, anatomy, healthcare documentation, and claim processing. Both medical and non-medical students can pursue this field with the right training and discipline.
Popular Medical Coding Courses in India
- Diploma in Medical Coding (6 months – 1 year)
- Certificate in Medical Billing and Coding
- Advanced Diploma in Healthcare Documentation
- Online training programs from AAPC or AHIMA-certified institutions
Many Indian institutes and online learning platforms such as Coursera, Udemy, and Medesun offer beginner-to-advanced level training in ICD-10 and CPT coding.
International Certifications in Medical Coding
To enhance credibility and job prospects, obtaining recognized certifications is highly recommended. The following are some of the most respected certifications for medical coders worldwide:
| Certification | Issuing Organization | Description |
|---|---|---|
| CPC (Certified Professional Coder) | AAPC (American Academy of Professional Coders) | Validates proficiency in CPT, ICD-10-CM, and HCPCS coding across outpatient facilities. |
| CCA (Certified Coding Associate) | AHIMA (American Health Information Management Association) | Entry-level certification ideal for beginners starting their coding career. |
| CCS (Certified Coding Specialist) | AHIMA | Recognized credential for coders handling inpatient or hospital-based medical records. |
| COC (Certified Outpatient Coder) | AAPC | Specializes in outpatient hospital and ambulatory surgical center coding. |
In India, many employers prefer certified professionals from AAPC or AHIMA because these certifications validate international-level skills. The CPC certification, in particular, opens doors to better-paying jobs and global opportunities.
Career Opportunities in Medical Coding
Medical coding has become one of the most promising and rapidly growing career options in the global healthcare sector. With the rising adoption of electronic health records (EHRs) and insurance-based healthcare systems, skilled coders are in high demand across hospitals, medical research centers, insurance companies, and outsourcing firms.
In India, many multinational companies and healthcare BPOs offer medical coding services to international clients, especially in the U.S., U.K., and Middle East regions. This global demand makes medical coding a stable and rewarding career choice for graduates from science, life sciences, and paramedical backgrounds.
Top Employment Sectors for Medical Coders
- Hospitals and Private Clinics
- Medical Billing Companies
- Health Insurance Providers
- Pharmaceutical Companies
- Medical Research Organizations
- Government Health Departments
- Healthcare BPO and IT Companies
Apart from traditional roles, coders can also progress into specialized areas such as coding auditing, medical data analysis, clinical documentation improvement, and compliance management. Many professionals also move into training, consulting, or quality assurance after gaining experience.
Average Salary of Medical Coders
The salary of a medical coder depends on various factors such as location, certification level, experience, and type of employer. Certified coders generally earn higher salaries compared to non-certified coders.
| Experience Level | Average Annual Salary (India) | Average Annual Salary (Abroad) |
|---|---|---|
| Entry-Level (0–2 years) | ₹2.5 – ₹3.5 Lakh per year | USD 30,000 – 45,000 per year |
| Mid-Level (3–6 years) | ₹4 – ₹6 Lakh per year | USD 45,000 – 60,000 per year |
| Senior-Level (7+ years) | ₹7 – ₹10 Lakh per year | USD 65,000 – 90,000 per year |
Professionals working for U.S.-based healthcare clients often earn higher packages due to international exposure and certification advantages. With experience, coders can also work as Medical Coding Auditors or Healthcare Data Analysts, both of which offer excellent growth potential.
Challenges in the Medical Coding Field
Although medical coding offers great opportunities, it also comes with specific challenges that require patience, accuracy, and continuous learning. Since healthcare laws and code sets are frequently updated, coders must stay informed and adaptable.
- Complex Documentation: Understanding and interpreting handwritten or incomplete clinical notes can be difficult.
- Constant Updates: ICD and CPT code sets are revised regularly, requiring ongoing education.
- Compliance Pressure: Coders must ensure compliance with healthcare regulations and avoid upcoding or undercoding.
- High Accuracy Expectations: A single coding error can result in financial loss or legal complications.
- Monotonous Work: Coding requires long hours of screen time and attention to detail, which may feel repetitive.
Despite these challenges, with dedication and regular upskilling, coders can maintain accuracy and stay competitive in the global market.
Future Scope of Medical Coding
The future of medical coding looks extremely bright, especially with the rapid digitalization of healthcare systems worldwide. As governments and private sectors continue to adopt electronic health records, the demand for skilled medical coders will continue to grow exponentially.
- AI-assisted Coding: Artificial intelligence is being integrated into medical coding software to improve speed and accuracy.
- Global Outsourcing: India has become a major outsourcing hub for U.S. and U.K. healthcare coding services.
- Data-driven Healthcare: Coders play a key role in collecting accurate health data for policy-making and research.
- Remote Work: Many medical coding jobs now allow work-from-home or hybrid setups, increasing flexibility.
- Integration with Health Analytics: Coders with data analytics skills are in high demand for healthcare research and predictive modeling.

According to several global healthcare reports, the medical coding and billing industry is projected to grow at a rate of over 10% annually in the coming decade. This indicates continuous job availability and strong career growth for certified coders across the world.
Conclusion
Medical coding forms the backbone of the modern healthcare system, linking clinical documentation with insurance and financial processes. It ensures that every patient encounter is recorded accurately, every claim is processed correctly, and every healthcare organization operates efficiently.
With proper training, global certifications, and continuous skill development, medical coding can be a secure and high-growth career path for students and professionals alike. Whether you’re from a medical or non-medical background, entering the field of medical coding opens the door to an international career with long-term stability and respect.
In conclusion, medical coding is not just about converting medical terms into numbers—it’s about ensuring transparency, accuracy, and efficiency in healthcare systems around the world.





